
What is Traditional Chinese Medicine?
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) is an ancient set of medical practices from China that operate under the belief that the processes of the human body are interrelated and connected to the environment. TCM practitioners approach healthcare from a holistic standpoint, looking for the underlying imbalances and disharmonies behind an illness. The practitioner will look at the whole picture and try to treat the patient, instead of just the disease.
What is the history of Traditional Chinese Medicine?
Traditional Chinese Medicine originated out of Taoist beliefs established over 4,000 years ago. Today TCM has been refined and adapted, but many of the practices are performed as they have been for thousands of years.
A theory of nature and of health and disease was set forth in the concepts of : two essential forces – Yin and Yang, three essences, five elements, six climatic influences, seven emotional factors, eight principles of therapy, fourteen-meridians, etc.
Traditional Chinese Medicine has always been an important component of healthcare in China, but over the past few decades, it has grown in popularity in the Western world as well. Today, practices such as acupuncture, Tai Chi and herbal treatments can be found in many health centers around the world, and scientific studies have shown promising health benefits.
Today, Chinese medicine represents a combination of ideas and methods from earlier times coupled with the findings from modern research methods, chemical analysis, pharmacological testing in the laboratory, and clinical trials. Chinese medicine is a major health care method in the People’s Republic of China, Taiwan, Hong Kong, Japan, Singapore, Vietnam, Thailand, Indonesia and other Asian Countries. Its apparent success there has led it to be adopted, in much smaller measure thus far, in South America, the U.S., Canada, and Europe.
Qi and Yin and Yang in Traditional Chinese Medicine
What is Qi?
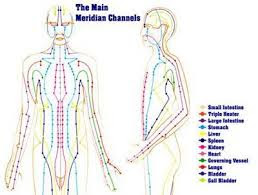
Central to TCM is the belief in an energy, known as Qi, which is roughly translated as “life energy.” Qi is believed to flow through a number of channels, or meridians, throughout the body, many of which follow major veins and arteries and connect to the internal organs to circulate Qi throughout the body. Qi can be described in many ways, according to the source, the location and the role it plays in the body. Regulating and stimulating the flow of Qi is a basic tenet of understanding the role of disease and health in the body.
What are Yin and Yang?
The terms Yin and Yang are used to describe the opposing conditions in the body, and come from the Chinese belief that all things have two aspects, which are at once opposite and interdependent. Practitioners believe that a balance of Yin and Yang is necessary for health.
Yin describes qualities that are dark, passive, feminine, receptive, and associated with the night. Yin is often symbolized by water or earth.
Yang describes qualities that are light, bright, active, masculine and associated with the day. Yang is symbolized by fire or air.
Within the body, each organ has qualities of both yin and yang, though some organs and functions may have more of one quality than the other. For instance, the heart is considered a yin organ, while the stomach is considered a yang organ.
What is the Five Elements Theory ?
Based on observations of the natural world, ancient Chinese people recognized continuous patterns of transformation and change in the universe.
Initially these observations were interpreted using Yin and Yang logic, but later they were expanded using the Five Elements Theory.
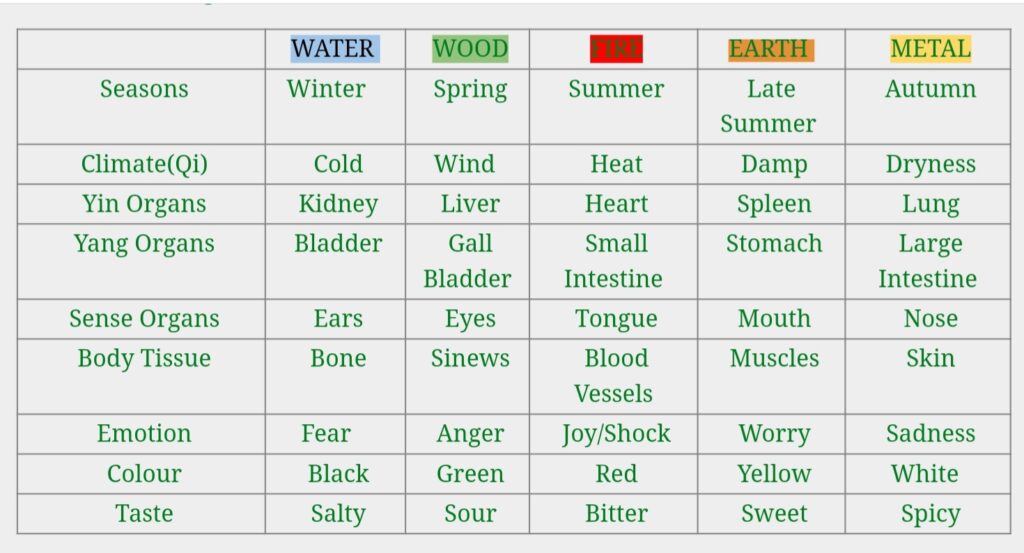
The Five Elements theory evolved from the study of various processes, functions and phenomena of nature. The theory asserts that substances can be dived into one of the five basic elements : WOOD, FIRE, WATER, METAL and EARTH, which each has their own specific characteristics and properties.
The Five Elements and their Relationship with Nature and the Body are illustrated in the following table :
Diagnosis According to Five Element Theory
The colors, emotions, flavors, senses, climates, body parts, and organs are all related. Through viewing the human body in this way, we can determine internal disharmony. For example, if a patient has a green hue to his complexion, a sour taste in his mouth, and his eyes are bothersome to him in some way, we would look more closely at the Wood element (Liver and Gallbladder).
What practices are used in Traditional Chinese Medicine?
All practices within Traditional Chinese Medicine revolve around the same set of beliefs and philosophies. Because it is a holistic, or complete health care system, it includes practices to govern diet and nutrition, exercise and spirituality along with the more specialized practices of acupuncture, acupressure, Tai Chi, Herbal Medicine and Qigong
Here are some links to understand more about acupuncture, acupressure, Tai Chi, herbal medicine, and Qigong.
Sources:
Mayo Clinic Book of Alternative Medicine. Time, Inc.
Alternative Healing: The Complete A-Z Guide to more than 150 Alternative Therapies by Mark Kastner, L.Ac., Dipl.Ac., and Hugh Burroughs. Henry Holt and Company: 1996
Traditional Chinese Medicine
Encyclopedia of Healing Therapies by Anne Woodham and Dr. David Peters.
http://scm.hkbu.edu.hk/en/home/index.php
Acupuncture
TCM Consultation :Please feel free to contact us at (852)93869048 to make an appointment for TCM consultation.
Agreement to Disclaimers :
By the use of this website, you confirm and agree to the statements and disclaimers set forth under the Disclaimer Page.The Website does not assume any responsibility for errors, inaccuracies or omissions in any of the articles or information posted on the website.








